Solidity
According to Solidity Docs, Solidity was proposed in 2014, it is an object-oriented and high-level programming language for implementing smart contracts.
- It governs the behaviors of accounts within the Ethereum state. Solidity is influenced by C++, Python, and JavaScript and is designed to target the Ethereum Virtual Machine(EVM).
- Solidity is also statistically typed, supports inheritance, libraries, and complex user-defined types among other properties.
- Solidity can be used to create contracts for voting, crowdfunding, blind auctions, and multi-signature wallets.
File Example
// storage.sol
Pragma Solidity ^0.6.0
Features of Solidity File
Pragma
The source file annotates Solidity compiler versions in three ways/syntax
- define specific solidity version
Pragma solidity 0.6.0;
pragma solidity ^ 0.6.0;
pragma solidity > 0.6.0 < 0.7.2;
Data Types
Stores different types of values I.e integer, boolean, array, enums, structure, mapping, address, comments
integer
There two types i.e signed and unsigned. signed integer stores positive and negative
int8
int16
int32
unsigned stores only positive integers.
uint8 to uint256
Boolean
Stores true or false. Commonly used to operate logic return negation, conjunction, and distinction. Uses the bool keyword
bool a = true
int b = 10
if (b < 20)
Array
Stores collection of something with the same data type. Fixed i.e Fixed length of elements and dynamic i.e no fixed size, controlled by push and pull function. Types of arrays and uses [] (square brackets).
Enums
Restrict to have one predefined values i.e Male and Female
Contract test {
Enum gender{Male, female, PreferNotToSay}
}
Structure
It's a complex data type. Solidity provides struct. It stores correlation of different data types for example student info has a name, age, gender, address, etc.
Struct {
int256 integer_name
String string_name
Uint unsigned_integer
}
Struct strut_name {
Type1 type_name_1
Type2 type_name_2
Type3 type_name_3
}
Mapping
Hash map refers to array and struct.
mapping(_KeyType => _ValueType) public mappingName
mapping (address => uint) public userLevel
function setCurrentLevel (address userAddress, uint level) public{
userLevel[userAddress] = level
}
function getCurrentLevel(address userAddress)
}
Address
Unique conception of solidity. An account or address is a 20 byte with 40 characters together with the 0x prefix. Address variable use address keyword and global variable: balance and transfer.
It's very informative in the creation of solidity.
Comments
Comment on code supports single line and multiple lines
// single line
/* multiple line */
Variables
Where variables will be stored. State variable i.e change contract permanently stored. Local variable i.e values are present until the function is executed. Global variables are special variables that exist in the global namespace used to get information about the blockchain and transaction properties. It is widely used to get information on the blockchain.
Variable Scope
The scope is where you can use i.e limited or global.
- public: in the contract or on another contract.
- internal: used within the contract and inheritance
- private: only used on the current contract
Operators
- Arithmetic Operators: operates integer variables for example math operators
-, +, %, /, ++ - Comparison Operator: boolean variables and integer variables
- Logic Operator: operate boolean operators
N between 0 and number && , || - Assignment Operator:
a = 1 += - Conditional Operator: to achieve a function eg
if statement ?:. Control structuralsLoops
There are 3 types: while, while do, and for. while loop: executes a statement in code block repeatedly by checking condition first.
While(expression) {
statement(s) toBeExpected if
expression isTrue
}
Do-While Loop
Checks the condition last execute statement first
do {
statement(s) toBeExecuted
} while (expression)
For Loop
Loop initialization to test statement condition using iteration.
for (initialization, test condition)
iteration statement {
statement toBeExecuted
// test condition is true
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
xxxxxxx
}
Skip the loop
Skip loop or iteration i.e break, continue(skip).
Decision-making using if, else, else if conditions. Choosing if-else allows solidity to make a correct decision out of several conditions.
uint a = 1
uint b = 2
uint c = 3
uint result
if(a > b && a > c) {
result = a;
}
else if
Functions
Group of reusable code that eliminates writing the same code again and again. Writing modular codes by dividing the big programs into a number of small and manageable functions.
Function function_name(parameter-list) scope(public/private) returns() {
//statements
}
Constructor
A function declared using constructor optional function. It is used to initialize state variables and it invokes the contract created.
constructor() {
uint a = 10.
uint b = 10
}
Modifiers for Functions
There are three types of modifiers: pure and view.
- Pure functions disallow modification/access state and there's no return. limitation: modifying state variable.
- View Function
- modifying state variable
- emitting events
- modifying state variable
- creating other contracts
- using self-destruct
Modifiers automatically check a condition prior to executing the function. Inheritance properties of contract and may be overridden by derived contracts.
modifier onlyOwner {
require(
msg.sender == owner()
"only owner can call this function"
);
}
Function Visibility
Visibility for functions of a contract. External: used in other contracts, not within i.e external function with this function_name
Events
Blockchain stores transaction blocks. Every transaction has a block representing solidity events that have occurred. Solidity defines events with the event keyword then arguments are placed in the blockchain.
pragma solidity >= 0.4.21 < 0.7.0;
constructor SimpleAuction{
event HighestBidIncreased(address, bidder, uint amount);
// event
function bid() public payable {
//
emit HighestBidIncreased(msg.sender, msg.value)
}
}
Building Smart Contract
// assignment.sol
pragma solidity ^ 0.6.0;
// store student information - uses structure
contract Test {
struct Student {
uint number;
string name;
bool isMale;
}
Student student1;
// memory- to use an array, mapping. No need for parameters new modifier (we need to see the result)
function setInformation(uint _number, string memory _name, bool _isMale) public {
student1.number = _number;
student1.name = _name;
student1.isMale = _isMale;
}
function getInformation() public view returns(uint, string memory, bool) {
return (student1.number, student1.name, student1.isMale);
}
}
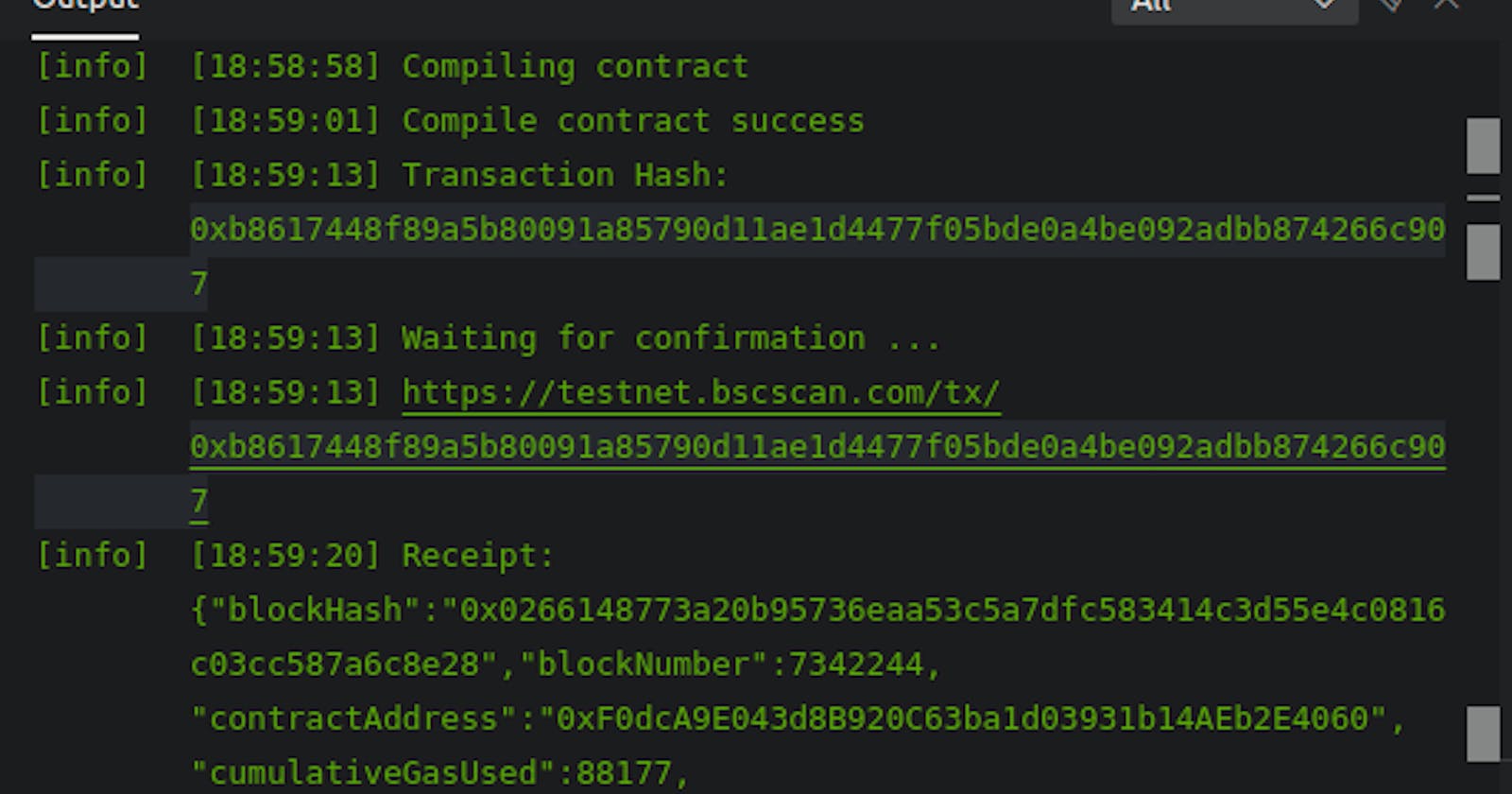
compile then deploy, interact and test on ChainIDE using metamask for deploy