How to create and deploy an ERC721 contract using OpenZeppelin Wizard, Ankr, Goerli, and Hardhat
In this article, we’re going to learn how to create an ERC721 NFT contract using the OpenZeppelin Wizard and later on compile and deploy it to Ethereum Goerli, Ankr protocol as our RPC Provider via hardhat.
OpenZeppelin Wizard
OpenZeppelin wizard generates an ERC20, ERC721, ERC1155, Governance contract that is customized or compiled and deployed directly by developers. It gives developers a chance to name the contract, and select the settings that they want on their contract. For example:
- if the contract will have features like:
- mint, burn, pause, permit, vote, flash mint, or snapshot for the ERC20 contract
- mint (with auto-increment of IDs), burn, pause, vote, enumerable, URI storage for ERC721 contract
- mint, burn, supply tracking & pausable for ERC1155 contract
- option to vote delay for the given voting period, proposal threshold, quorum, token decimals, whether it will have updatable settings or will be bravo compatible for Governance Contract.
- give access control to either ownable or specific roles
- determine the upgradability of the contract i.e Transparent or UUPS
- the license identifier which by default is MIT
Creating Contract on Wizard
- Visit the OpenZeppelin Wizard site
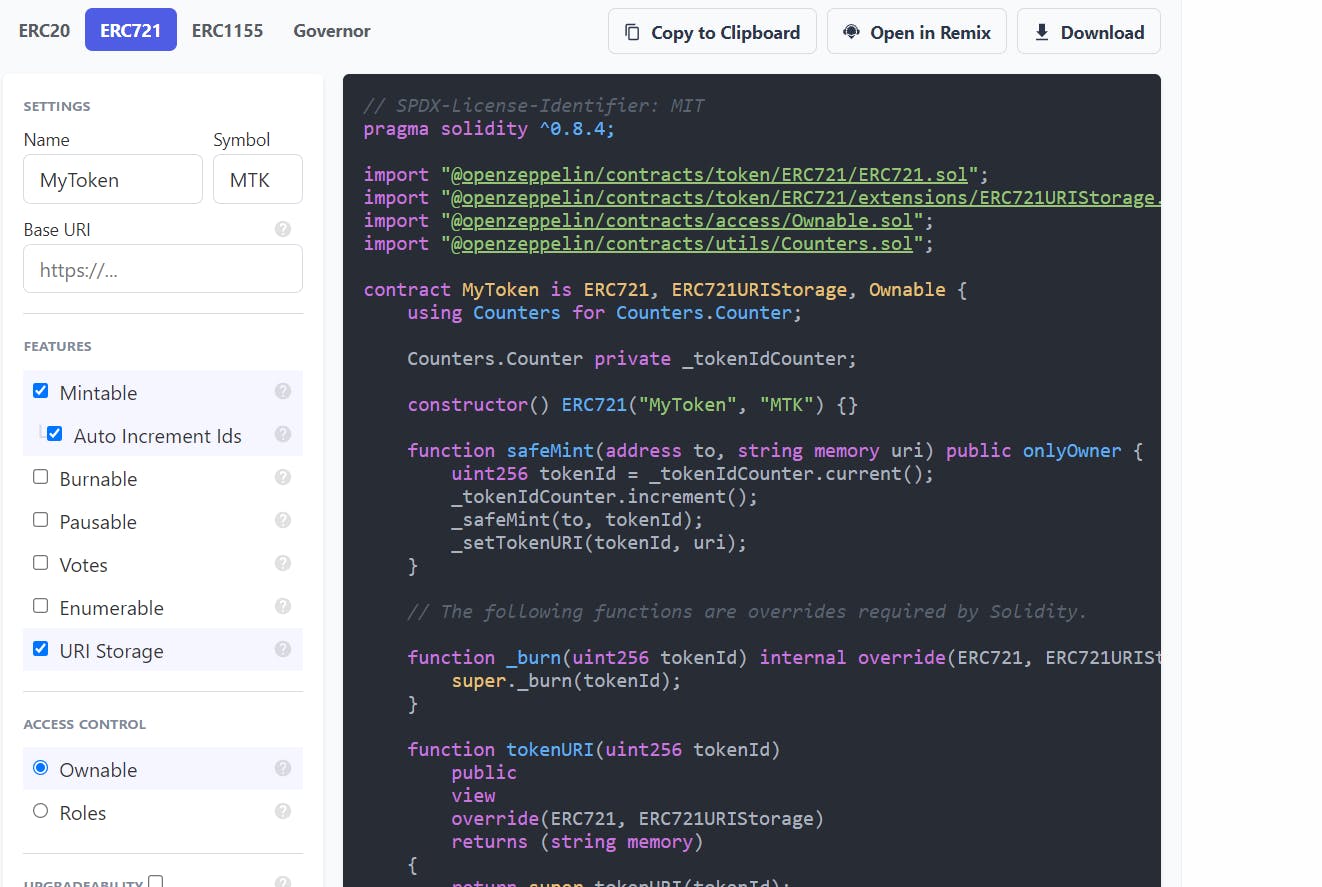
- We’ll select ERC721 on top then move to settings where we’ll give our contract a name
Madarakaand a symbolMDR, determine the pre-mint number then move features we’ll selectMintablewithauto-increment IdsandURI Storage. It will be Ownable by default and use the MIT license identifier. At this point, we’ll have successfully created our main contract:
Setting up Project Folder and Hardhat
We’ll move ahead and set up our project folder locally and we’ll use Hardhat as our development environment to compile and deploy our contract. For this step, you’ll need a node environment already set up on your local computer since we’ll use npm packages. If you don’t have the node installed you can check here on here to download node.js and if you’re not sure you can check node —version on your terminal.
Create a folder on your favorite IDE, personally, I will use vs code
$ mkdir ERC721MTK
$ cd ERC721MTK
$ code .
Install Hardhat
Hardhat is an Ethereum development environment that allows developers to write, compile, write tests, and deploy their smart contracts. You can hardhat documentation for installations instructions and other configurations you might need while working with hardhat:
Inside our ERC721MTK folder, we’ll configure hardhat:
$ npx hardhat
888 888 888 888 888
888 888 888 888 888
888 888 888 888 888
8888888888 8888b. 888d888 .d88888 88888b. 8888b. 888888
888 888 "88b 888P" d88" 888 888 "88b "88b 888
888 888 .d888888 888 888 888 888 888 .d888888 888
888 888 888 888 888 Y88b 888 888 888 888 888 Y88b.
888 888 "Y888888 888 "Y88888 888 888 "Y888888 "Y888
Welcome to Hardhat v2.9.1
? What do you want to do? ...
> Create a basic sample project
Create an advanced sample project
Create an advanced sample project that uses TypeScript
Create an empty hardhat.config.js
Quit
// We'll select create a basic sample project since it's selected by default press enter
// install hardhat, @nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle, ethereum-waffle, chai, ethers
$ npm install --save-dev "hardhat@^2.9.1" "@nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle@^2.0.0" "ethereum-waffle@^3.0.0" "chai@^4.2.0" "@nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers@^2.0.0" "ethers@^5.0.0"
since we’re using OpenZeppelin Contracts we’ll need to install OpenZeppelin on our project folder
$ npm install @openzeppelin/contracts
Now hardhat is set up, we’ll go to the contracts folder and rename the Greeter.sol, file to Madaraka.sol, and clear the code on the file. We’ll go back to OpenZeppelin wizard and copy the contract we had created and come and paste it to our contract file on our project folder.
// Madaraka.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.4;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/ERC721.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721URIStorage.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/access/Ownable.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Counters.sol";
contract MyToken is ERC721, ERC721URIStorage, Ownable {
using Counters for Counters.Counter;
Counters.Counter private _tokenIdCounter;
constructor() ERC721("MyToken", "MTK") {}
function safeMint(address to, string memory uri) public onlyOwner {
uint256 tokenId = _tokenIdCounter.current();
_tokenIdCounter.increment();
_safeMint(to, tokenId);
_setTokenURI(tokenId, uri);
}
// The following functions are overrides required by Solidity.
function _burn(uint256 tokenId) internal override(ERC721, ERC721URIStorage) {
super._burn(tokenId);
}
function tokenURI(uint256 tokenId)
public
view
override(ERC721, ERC721URIStorage)
returns (string memory)
{
return super.tokenURI(tokenId);
}
}
Compile the contract
$ npx hardhat compile
Compiled 13 Solidity files successfully
Setting Up the .env and hardhat.config.js file
create a .env file where we can save our development variables
- To create our RPC Provider URLs we’ll visit Ankr Protocol for Public RPCs for this contract I have opted for Ethereum then select Testnet on provider URLs. For Ethereum Test-net I have opted for Goerli but you can use Rinkeby or Ropsten. We’ll copy the RPC URL shown below Goerli and add it to our
.envfile
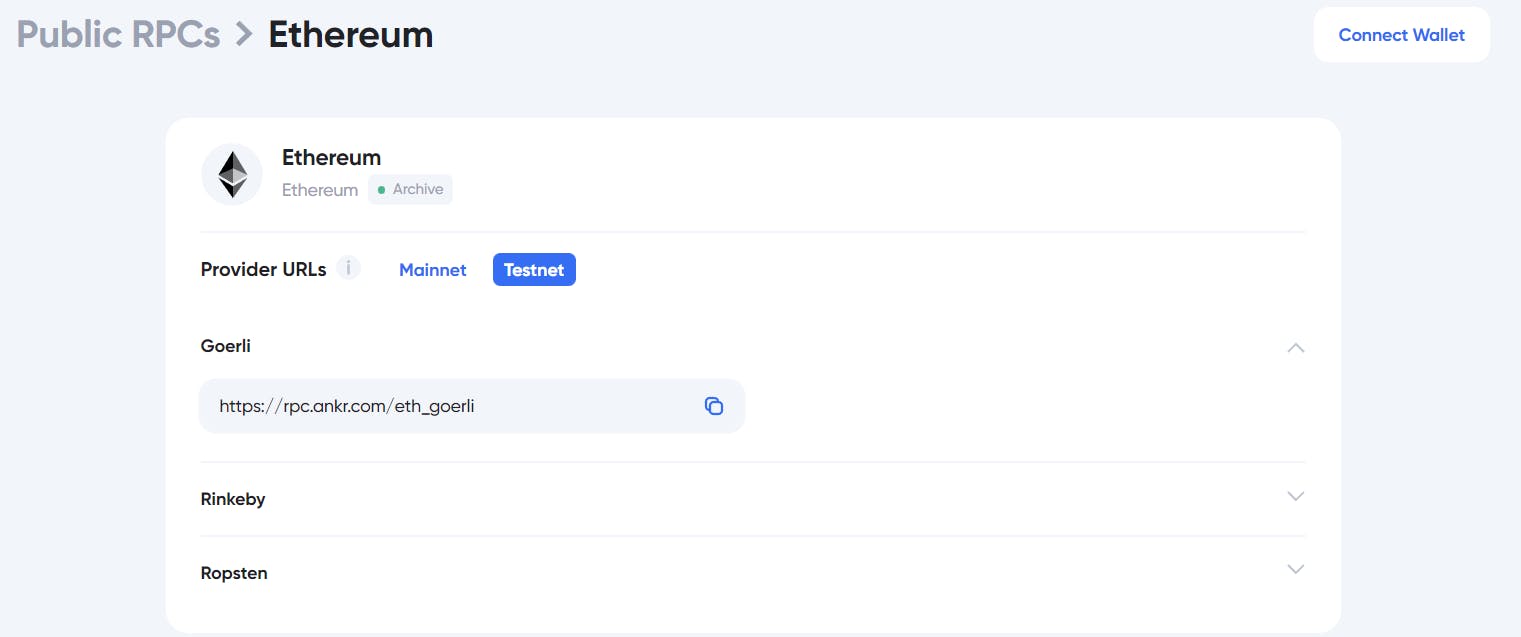
RPC_URL='https://rpc.ankr.com/eth_goerli'
Open your Metamask and switch account to Goerli. If you:
- don’t have Metamask extension installed in your browser you Install Metamask here.
- need Goerli faucets you can get some Goerli here by connecting your Alchemy Account or through the Chainlink faucets select ETH Goerli then paste the address
don’t have Goerli network added to your Metamask you can add using the details below
Network Name: Goerli New RPC URL: Chain ID: 6284 Currency Symbol(Optional): Goerli
Check your Goerli Test Network, select the three dots beside the account then select Account details then select private key you’ll enter your password then click confirm inorder for the account private key to be displayed. Copy the private key and add to your .env file and ensure to keep it private. The .env file should be added on .gitignore so the environment variables are not pushed to github for security purposes.
RPC_URL='https://rpc.ankr.com/eth_goerli'
PRIVATE_KEY=''
Lets’s now go ahead and setup our hardhat.config.js file. We’ll need to install dotenv.
$ npm i dotenv
You can configure you hardhat.config.js file this way
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle");
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-etherscan");
const dotenv = require("dotenv");
dotenv.config({path: __dirname + '/.env'});
const { RPC_URL, PRIVATE_KEY } = process.env;
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers")
// task("accounts", "Prints the list of accounts", async (taskArgs, hre) => {
// const accounts = await hre.ethers.getSigners();
// for (const account of accounts) {
// console.log(account.address);
// }
// });
module.exports = {
solidity: "0.8.4",
networks: {
goerli: {
url: RPC_URL || "",
accounts: PRIVATE_KEY !== undefined ? [PRIVATE_KEY] : [],
},
},
};
compile to contract to confirm if there are any errors
$ npx hardhat compile
If there are no errors we will go ahead and deploy our contract to ETH Goerli. We’ll first set up the deploy.js file on a script by renaming the contract name or configure it this way:
// We require the Hardhat Runtime Environment explicitly here. This is optional
// but useful for running the script in a standalone fashion through `node <script>`.
//
// When running the script with `npx hardhat run <script>` you'll find the Hardhat
// Runtime Environment's members available in the global scope.
const hre = require("hardhat");
async function main() {
// Hardhat always runs the compile task when running scripts with its command
// line interface.
//
// If this script is run directly using `node` you may want to call compile
// manually to make sure everything is compiled
// await hre.run('compile');
// We get the contract to deploy
const MyToken = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("MyToken");
const myToken = await MyToken.deploy();
await myToken.deployed();
console.log("MyToken deployed to:", myToken.address);
}
// We recommend this pattern to be able to use async/await everywhere
// and properly handle errors.
main()
.then(() => process.exit(0))
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exit(1);
});
At this step, we’ll deploy our contract to the testnet
$ npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network goerli
MyToken deployed to: 0x617b397207b38Db7e7b6445f57373c23B5e8322c
We have successfully deployed our contract. We can’t verify the contract and interact with it since we didn’t set up Etherscan in our configurations but in the next tutorials, we’ll add that. You can only check the deployed contract here on Goerli EtherScan.
This is the summary of the tutorial on how to create the ERC721 contract on OpenZeppelin Wizard and deploy it to Ethereum Goerli using Ankr as our RPC URL provider. You can check the full code here on Github.
Thank for reading through my article you can leave any comments or suggestions. We can also connect more on Twitter or LinkedIn.
