In this article, I’m going to write about how one can get started with Vue.js, especially for one who already has experience with Javascript and other Javascript frameworks like React.
I recently had a take-home assignment that required me to use Vue.js I asked if I could use React but they said it's strictly a Vue.js task. Prior to this, I had never worked with Vue.js on a personal project or directly. I have been seeing conversations around Vue.js in the tech community, I have attended a Vue.js meetup twice and got to learn a couple of details without practicing.
Writing this based on my personal since there’s a way Routing, and Components work in different versions of Vue eg Vue3 or there are special ways of installing different packages and setting them up within the Vue project.
Installation
Prerequisites
Have node.js installed depending on your operating system: check here for details
package managers like npm or yarn installed
install Vue package
npm i vue
I’m going to talk about two ways in which you can set up a new Vue.js project:
Using Vue.js Documentation
The first one is through the Vue.js Documentation you’re given a clear path to set up a project.
npm init vue@latest
You will be expected to enter the project name and select whether you want to add Typescript, JSX, Vue Router, Pinia, Vitia, different end-to-end testing libraries, Eslint or Prettier.
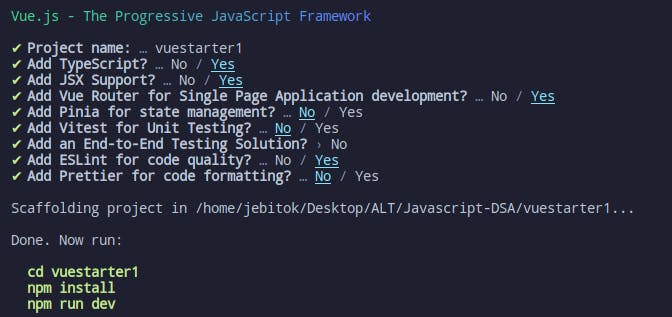
What is important depends on your project but as a beginner in Vue, the biggest priority is having Router and JSX. If you're comfortable with Typescript and Eslint it can work well too the challenge comes when you're still figuring out the Vue.js folder arrangement and how to handle errors you'll encounter for example missing components, wrong imports, etc before you come to syntax errors and cleaner code
Once you've installed it, you can run the sample template and start making changes to the project either JSX or the Template. With time you'll get a way around it.
Using Vite
Vite allows you to start a different project, especially Javascript libraries and allows you an option to add different languages e.g. Javascript or Typescript, It also helps you with code bundling, and fast dev server among other features. It's amazing to get used to.
To create a basic Vue.js project:
npm create vite@latest
// Vue
// Javascript or Typescript variant
Vite allows you to select multiple options either scaffold a project with Javascript, typescript or customize with create-vue(like the previous example above).
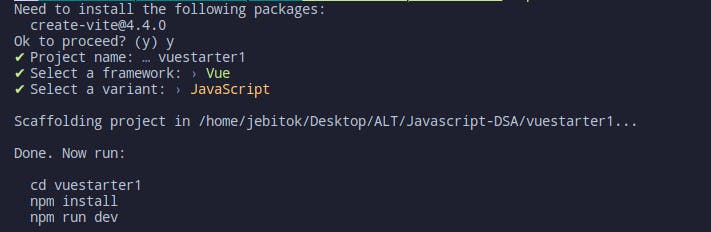
With this one, I picked the Javascript Variant, it is a nice way to start a project but the only challenge with it you'll need to set up the Vue router on your own.
npm create vite@latest
// Vue
// Customize with create-vue
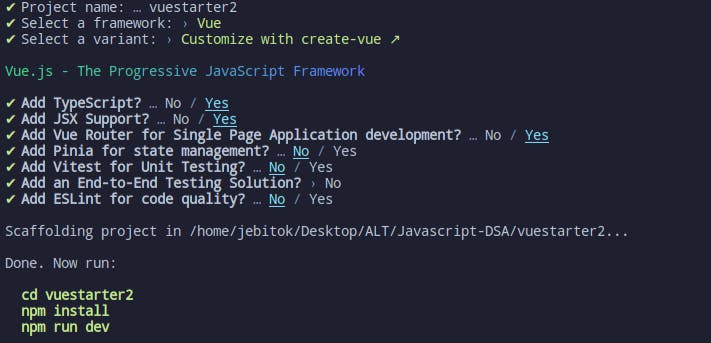
Vue Router and Components
To understand the basics of Vue router in case you scaffold a project that doesn't have one the best way to navigate through this challenge is to check the Vue.js documentation on Vue Router they have example projects.
For Components, this was introduced in Vue3, especially for React.js developers this is something we are more used to especially when you want to pass data through a component. You can also check Vue.js Docs on Components Registration and tutorials either articles or on YouTube.
Basic Vue Folder structure
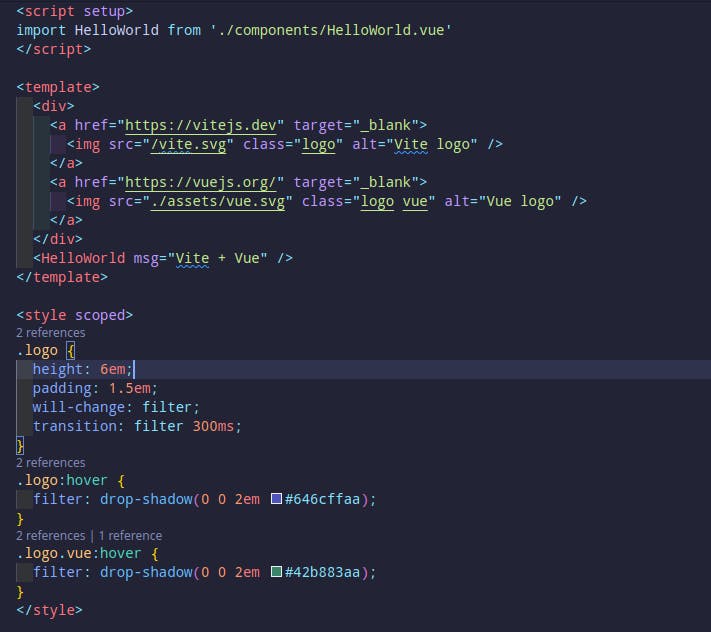
This is how a basic Vue.js file is structured it has the:
Script:
import other files/components that you will be routing or reusing
import other npm packages that you might have installed
allows you to specify a file name, pass data, and the components
write some functionality that will be used within the template section e.g the handleClick function for a button
Template:
- the template is like the JSX in React where you pass the basic HTML element and CSS classes. Unlike JSX in React, the Javascript logic is minimal within this section for cases like rendering, Vue will use inbuilt directives e.g. v-if, v-else etc, unlike the if-else or map statements or methods in React.
Style:
this allows you to write your own styling within the same file and not in-line styles.
If you manage to set up Tailwind CSS or Bootstrap within the Vue.js app the class names will also be used as per the CSS framework and you won't have to write a lot of CSS within the style section.
Learning a New Framework
Generally out of my recent situation of starting to work with Vue.js on two separate projects. I have learned:
Vue.js is a nice framework and I should have started exploring it earlier
Project requirements might always affect the framework or library that you will use React, Vue.js, Angular, or Next.js among others have grown in JS frontend development.
Always consider exploring another framework/library linked to your program language as it's helpful for you to gain familiarity with basic project installation, folder structure, and basic functionalities or features e.g. routing, components, passing data, styling, etc. You won't have to take a lot of time to pick up a project as you already know the basics of that framework or library
Thank you for reading through the article. It might lack full comprehension this is just to help you get started. You can leave a comment, like, or suggestion, especially on resources or future article topics. We can connect more on Linkedin or Twitter. Thank you!
